| Ceramic materials that are designed to have the special conditions required for the modern industry and made to have new functions, using highly pure raw materials for artificial synthesis.
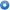 Classification of Precision Ceramic Materials Classification of Precision Ceramic Materials
The following is the most common way of classifying precision ceramic materials by their function.
 Electromagnetic Functional Materials Electromagnetic Functional Materials
1)
High insulating properties: Integrated circuit boards
2)
Inducing properties: High-capacity capacitor
3) Piezoelectricity: Resonators, ignition devices
4)
Pyroelectricity: Infrared-ray sensor devices
5)
Soft magnetic property: Memory operation devices, magnetic tape
6)
Hard magnetic property: Magnets
7)
Semiconductivity: Sensors, thermistors, heating elements
8)
Ion conductivity: Batteries, oxygen sensors
9) Electronic radioactivity: Electronic tasers, thermionic cathodes
10)
Superconductivity: Memory elements, circuits
 Optical Functional Materials Optical Functional Materials
1) Fluorescence: Fluorescent substances
2)
Translucence: High-pressure sodium, etc.
3)
Optical reflectivity: Solar heat collector
4)
Light guiding: Optical communication cables
5)
Light proof: Useful for blocking infrared rays
 Biochemical Functional Materials Biochemical Functional Materials
1) Substitute materials for aggregates
2)
Carriers for control of chemical reactions
3)
Chemical reaction catalysts
 Thermal Functional Materials Thermal Functional Materials
1)
Materials with heat resistant structures
2)
Lightweight insulating materials
3)
Heat-transmitting materials
 Mechanical Functional Materials Mechanical Functional Materials
1)
Strength-enhanced materials
2) Wear-resistant functional materials
 Nuclear-Related Functional Materials Nuclear-Related Functional Materials
1)
Nuclear fuel, moderators, reflective agents, controllers, nuclear reactor materials, etc.
|